 |
Wat is RPA, de definities
McKinsey:Leslie Willcocks: RPA takes the robot out of the human. The average knowledge worker employed on a back-office process has a lot of repetitive, routine tasks that are dreary and uninteresting. RPA is a type of software that mimics the activity of a human being in carrying out a task within a process. It can do repetitive stuff more quickly, accurately, and tirelessly than humans, freeing them to do other tasks requiring human strengths such as emotional intelligence, reasoning, judgment, and interaction with the customer.
Symphony:
A capability that comprises of software and services that enables you to perform complex rule based work and integrate with any system to perform work in the same way as people do
Aan de ene kant heb je macro's en screenscrapingstoosl en aan andere kant heb BPM-tools. Het heeft de decision- en worklflowtools van een BPM-applicatie, maar het heeft ook veel integratietools.
In het volgende schema staat aangegeven waar robotic-tools staan ten opzichte van andere tools.
Waar komt RPA vandaan?
Het bedrijf Blue Prism introduceerde term in 2012. Ze schrijven daaroverWhen Blue Prism coined the term “RPA” back in 2012, it applied to a new breed of enterprise scale, dynamic automation that we had developed by working closely with our clients. One that was able to reproduce the exact actions of a human operator; using the same interfaces, reproducing the same complex decisions, “seeing” what the human operators performing that task manually were seeing, adapting to variations in performance, environmental factors and changing data."
In The Evolution of the RPA Market, schrijft Softmotive
RPA’s origins lie in older technologies such as workflow automation and screen scraping. From early examples of the first learning robots, such as General Robotics Corp’s RB5X in 1984, to the AI chatbot Jabberwacky in 1988, RPA’s roots stretch back decades. However, many of these developments were more valuable from a research perspective than from a business perspective. Many business applications of these technologies that were attempted had a reputation for being unreliable, inflexible or difficult to use.
As technology advanced, the value of RPA became more apparent. One of the most significant examples of how RPA was evolving into a practical, extremely powerful tool was IBM’s Watson, developed in 2006. This solution showed that an automated system could gather information, solve problems and interact in human-like ways.[ii] As underlying technology evolved, solution providers began to develop more effective tools, combining these technologies into more useful, practical packages. This gave rise to RPA as we know it now: an intuitive, robust set of tools that allows companies to automate a wide range of processes.
However, many were slow to implement new RPA solutions, believing them to be more hype than substance. A reliance on the proven benefits of offshoring to drive increased efficiency coupled with a distrust of new technology slowed adoption. Now, as RPA solutions have proven themselves and enterprises are looking for ways to manage growing worldwide labor costs, companies are finally deploying automation.
Is RPA Artificial Intelligence?
Er wordt onderscheidt gemaakt tussen twee soorten RPA.1. Traditionele RPA - dat zijn de 'gewone' regelgebaseerde systemen
2. Cognitieve RPA - dit zijn de systemen die NLP (natural language processing) en AI, zoals ML (machine learning) intregeren.
De eerste is uiteraard geen AI.
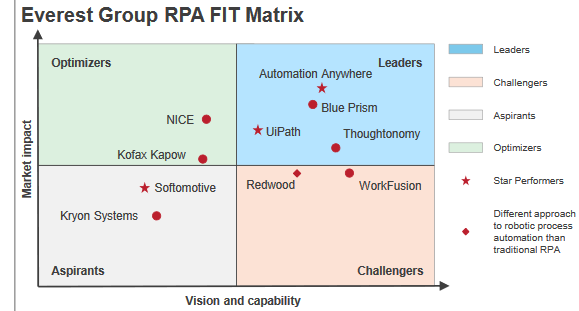
De ranking van de tools
The Forrester Wave™: Robotic Process Automation, Q1 2017The 12 Providers That Matter Most And How They Stack Up
– Technologies for Building a “Virtual Workforce”
Termen: Robot versus een bot
Een robot is een programmeerbare machine die verschillende taken uit kan voeren (bron wikipedia)Ann Delmedico (Prudential) hanteert de volgende definities.
- Robots - Een robot is datgene wat ons 24 uur capaciteit geeft. Je huurt niet iemand voor een job voor 10 minuten, als iemand 8 uur beschikbaar is. Dan gebruik ze voor 8 uur. Robots bestaan dus uit bots.
- Bots - zijn geautomatiseerde taken of processen. Je kunt processen draaien op een robot. Iemand kan zeggen ik heb 100 robots draaien, maar ze gebruiken het alleen voor 10 uur werk. Het gaat erom dat je de capaciteit van de robot goed gebruikt.
Waarvoor gebruik je RPA
Reden:- Voor sommige is het niet kunnen groeien, zonder iedere keer nieuw personeel aan te nemen.
- Kostenbesparing.
- De mogelijkheid uit de weg te gaan om het werk naar het buitenland om werk te outsources.
In het artikel The Rise of Robots, schrijft de bank BNY Mellon
It takes a human five to 10 minutes to reconcile a failed trade. A bot can do it in a quarter of a second.
Bots are also used in data-reconciliation, enabling the team to focus on exceptions and quality control.
Wij hanteert de volgende definities.
- Robots - Een robot is datgene wat ons 24 uur capaciteit geeft. Je huurt niet iemand voor een job voor 10 minuten, als iemand 8 uur beschikbaar is. Dan gebruik je ze voor 8 uur.
- Bots - zijn geautomatiseerde taken of processen. Je kunt processen draaien op een robot. Iemand kan zeggen ik heb 100 robots draaien, maar ze gebruiken het alleen voor 10 uur werk. Het gaat erom dat je de capaciteit van de robot goed gebruikt.
Zie webinar
Interessante links
- Top 10 Hot Artificial Intelligence (AI) Technologies
- First Consulting helpt financiële sector met Robotic Process Automation
- Is Artificial Intelligence the next big change the financial sector should prepare itself for? 1 day Conference Artificial Intelligence The next shift in Finance and Risk - 29th of March 2018
- ABN AMRO Startup Friday | Robotics
- Rabobank: a future robot bank? - Artificial intelligence (met IBM Watson)
- Robotics in Finance - Creëer ruimte voor kwaliteit | ABN/Amro
- RPA and AI Summit 2016: Rabobank ICT Interview



Reacties
Een reactie posten